Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a common neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by persistent difficulties with attention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. While commonly diagnosed in childhood, it can persist into adulthood and significantly impact various aspects of life.
Understanding the Spectrum of ADHD:
ADHD is not a monolithic condition but rather a spectrum with varying presentations. It can be categorized into three main types:
- Predominantly Inattentive (ADHD-PI): Difficulty focusing, staying organized, and following through on tasks characterizes this type. Hyperactivity and impulsivity may be less pronounced or absent.
- Predominantly Hyperactive-Impulsive (ADHD-HI): Excessive fidgeting, talking, and difficulty staying still define this type. Attention difficulties may be present, but less noticeable than in the inattentive presentation.
- Combined Presentation (ADHD-C): This type encompasses symptoms of both inattentiveness and hyperactivity-impulsivity.
Symptoms and Their Impact:
Inattentiveness:
- Difficulty focusing on tasks and conversations
- Frequent daydreaming and mind-wandering
- Easily distracted by internal and external stimuli
- Organization challenges, misplaced items, and forgetfulness
- Incomplete tasks and deadlines missed
Hyperactivity-Impulsivity:
- Fidgeting, squirming, and excessive movement
- Talkativeness and difficulty staying quiet
- Impulsive actions without considering consequences
- Difficulty taking turns and waiting patiently
- Emotional outbursts and challenges with frustration tolerance
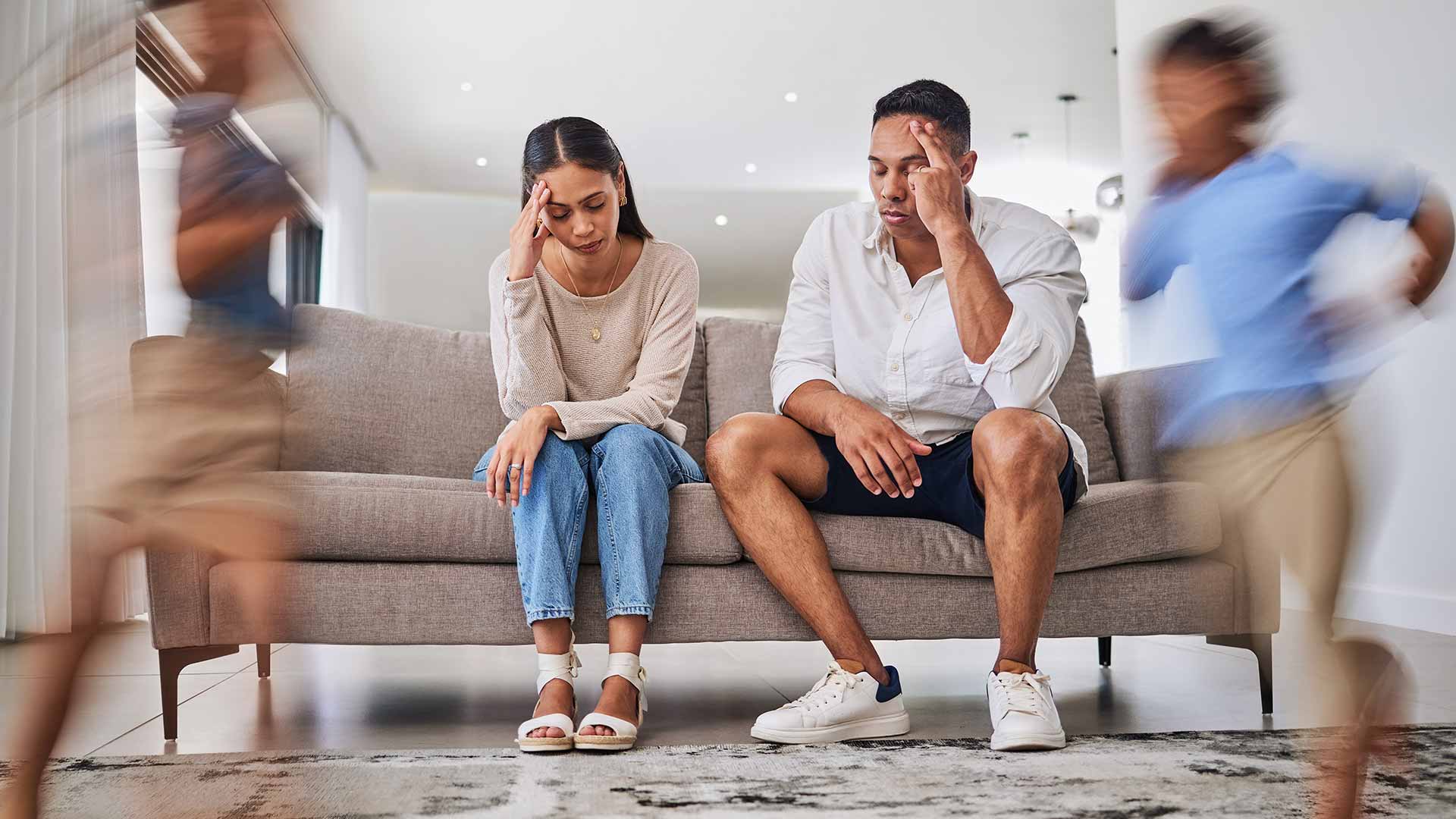
These symptoms can significantly impact various aspects of life, including:
- Academic performance: Difficulty focusing in class, completing assignments, and maintaining organization can lead to learning challenges.
- Social relationships: Impulsivity, inattention, and hyperactivity can hinder social interactions and building relationships.
- Self-esteem: Challenges with organization, meeting deadlines, and managing emotions can impact self-confidence and self-esteem.
- Work performance: Difficulties with time management, focus, and impulsivity can create challenges in professional settings.
Diagnosis and Management:
Diagnosis of ADHD requires a comprehensive evaluation by a qualified mental health professional. This typically involves gathering information from the individual, family members, and sometimes teachers or other relevant professionals. The evaluation may include cognitive assessments, clinical interviews, and behavior rating scales.
Currently, there is no cure for ADHD; however, effective management strategies can significantly improve symptoms and quality of life. These include:
- Medication: Stimulant medications are often prescribed to improve focus and attention. Other medications may be used to address specific symptoms like impulsivity or anxiety.
- Psychotherapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a commonly used therapy approach that helps individuals develop coping mechanisms, organizational skills, and emotional regulation strategies.
- Support groups: Connecting with others who understand the challenges of ADHD can be invaluable for support, encouragement, and sharing experiences.
Living with ADHD:
Individuals with ADHD can lead fulfilling lives by understanding their unique needs and accessing appropriate support. Effective management strategies, combined with individual strengths and talents, can enable them to thrive in different aspects of life.
OrbRom Center recognized as a leading provider of special education services in Phnom Penh, offers comprehensive support for individuals with ADHD and their families. Their team of experienced and qualified professionals provides a holistic approach encompassing:
- Diagnosis and Assessment: Utilizing standardized tools and a multi-disciplinary approach, OrbRom offers accurate and reliable diagnosis of ADHD, ensuring individuals receive the appropriate support.
- Individualized Education Plans (IEPs): Tailored to each student’s unique needs and strengths, IEPs incorporate evidence-based strategies to address core ADHD challenges in academics, social skills, and emotional regulation.
- Behavioral and Cognitive Interventions: OrbRom employs a range of interventions, including cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and mindfulness training, to equip individuals with ADHD with self-management skills and emotional regulation strategies.
- Family Support and Training: Recognizing the crucial role of families in supporting individuals with ADHD, OrbRom provides psychoeducational workshops and support groups to empower families with knowledge and effective strategies.
- Collaborative Approach: OrbRom works closely with schools, communities, and other healthcare professionals to create a comprehensive support network for individuals with ADHD and ensure their success in all aspects of life.



Leave A Comment