Dyslexia is a learning difference that primarily affects reading, writing, and spelling. However, fatigue is a common complaint among individuals with dyslexia, and it can significantly impact their daily lives. This blog explores the potential connection between dyslexia and fatigue, examining the various factors that might contribute to this experience.
Increased Cognitive Effort
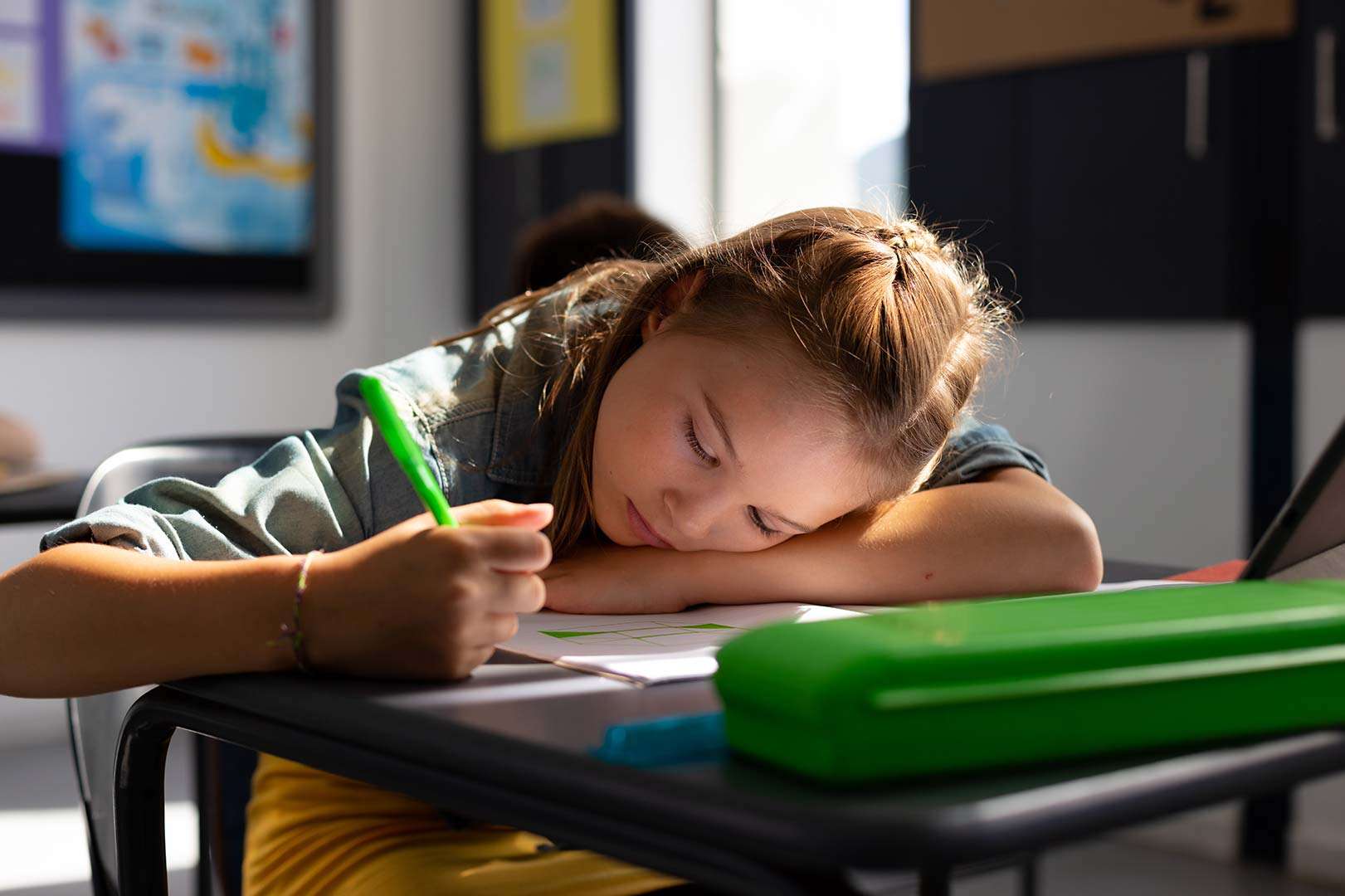
The core challenge of dyslexia lies in processing written language. Decoding words, maintaining focus while reading, and following written instructions all require more cognitive effort for individuals with dyslexia compared to neurotypical individuals. This extra mental exertion can lead to fatigue, especially during extended periods of reading or writing.
Visual Processing Challenges
Some individuals with dyslexia experience visual stress, which can make reading physically tiring. Text may appear blurry, distorted, or jump around on the page, causing discomfort and straining the eyes. This visual discomfort can contribute to fatigue and headaches, making it difficult to sustain focus.
Stress and Anxiety
The constant effort required to navigate a world heavily reliant on written language can be a source of stress and anxiety for individuals with dyslexia. This emotional burden can manifest as physical fatigue, making it even harder to concentrate and complete tasks.
Sleep Disruption
The frustration and stress associated with dyslexia can negatively impact sleep quality. Difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, and experiencing restless nights can further exacerbate fatigue and hinder daytime functioning.
Underlying Conditions
In some cases, fatigue experienced by individuals with dyslexia may be linked to underlying medical conditions like iron deficiency, sleep apnea, or thyroid disorders. A thorough medical evaluation can help rule out any contributing factors.
Impact on Daily Life
Fatigue associated with dyslexia can significantly impact daily activities. Students may struggle to stay focused during class, find it difficult to complete homework assignments, and experience lower academic performance. Adults with dyslexia may experience difficulty concentrating at work, have reduced productivity, and experience difficulty managing daily tasks.
Management Strategies
While there is no cure for dyslexia, there are strategies that can help manage fatigue and improve overall well-being. These include:
- Prioritizing good sleep hygiene – Establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensuring a sleep-conducive environment can significantly improve sleep quality.
- Incorporating breaks – Scheduling regular breaks during periods of reading or writing can help prevent mental strain and reduce fatigue.
- Utilizing assistive technology – Text-to-speech software, audiobooks, and colored overlays can make reading tasks less demanding and reduce visual stress.
- Stress management techniques – Relaxation techniques like meditation or deep breathing exercises can help manage stress and anxiety, which can contribute to fatigue.
- Seeking professional support – Therapists can teach coping mechanisms to manage the emotional challenges associated with dyslexia.
Fatigue is a common experience for many individuals with dyslexia. Understanding the factors that contribute to this symptom is crucial for developing effective management strategies. Through a combination of self-care practices, assistive technology, and professional support, individuals with dyslexia can learn to manage their fatigue and live fulfilling lives.




Leave A Comment